Table of Contents
X4D Overview
The DSX Suite application X4D tracks 3D objects (bones, implants, etc.) in X-ray images by generating digitally reconstructed radiographs (DRRs) of the objects and matching them to the X-ray images. It requires that the 3D X-ray configuration parameters be defined in the subject file and that the X-ray images be corrected. Matching DRR images to X-ray images requires both sets of images to be processed first.
- X-ray images are smoothed with a convolution filter and then an edge detection algorithm is run. The final processed X-ray image used for tracking is the edge detection image times a weighting factor, plus the smoothed intensity image.
- DRR images are not smoothed but are input to the edge detection algorithm. The final processed DRR image is the edge detection image time a weighting factor, plus the original DRR image.
X4D has a job batch option, enabling multiple tracking optimizations to be run without user intervention.
Tutorials
User should start with this initial tutorial to begin using X4D:
Once the initial tutorial is complete, three “How To” tutorials are available for specific processes within X4D:
Bone Tracking
Read the following pages to understand the bone tracking processes you are implementing in X4D:
Motion Capture Data
Learn how to work with motion capture data in X4D.
Image Metrics
These image metrics are used by X4D's optimization algorithm to compare the X-ray and DRR images during object tracking:
Menus
The X4D application contains six menus: File, View, Queue, Pose Maps, Options, and Help.
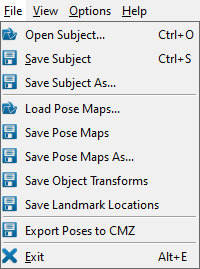
File Menu
- Open Subject… (Ctrl + O) This command loads a subject file.
- Save Subject (Ctrl + S) This command saves the currently loaded subject to its existing subject file.
- Save Subject As… This command saves the currently loaded subject to a new subject file.
- Load Pose Maps… This command loads an existing pose map file for each selected object. You will be prompted to browse for each file, which must be saved as a .csv file.
- Save Pose Maps This command saves the pose map of each selected object in the current trial to a .csv file. This file contains 6 values for each pose: the XYZ translation and the XYZ Euler angles representing the transform from the X-ray lab frame to the object's local coordinate system (i.e., as if you were traveling from the lab frame to the object frame). If a name for the pose map file is not already specified in the subject file, you will be prompted to browse for the file to create. A link to this file will then be added to the subject file.
- Save Pose Maps As… This command saves the pose map for each selected object in the current trial to a new .csv file. You will be prompted to browse for a new file for each object. A link to this new file will then be added to the subject file.
- Save Object Transforms This command saves the pose map of each selected object in the current trial to a .txt file. This file contains a 4×4 transform for each pose, expressing the transform from the X-ray lab frame to the object's local coordinate system (i.e., as if you were traveling from the lab frame to the object frame). If a name for the transforms file is not already specified in the subject file, you will be prompted to browse for the file to create. A link to this file will then be added to the subject file.
- Save Landmarks This command saves the locations in the X-ray lab frame of each selected object's landmarks in the current trial to a .txt file. This file contains a set of landmark coordinates for each pose in the pose map. If a name for the landmarks file is not already specified in the subject file, you will be prompted to browse for the file to create. A link to this file will then be added to the subject file.
- Export Poses to CMZ This command exports the pose map of each selected object in the current trial to the session's CMZ file. If the CMZ already contains poses for these objects for this trial, those poses will be removed before the current ones are exported. This command does not affect the poses of unselected objects, nor of other trials in the CMZ file. If a CMZ file is not already specified in the subject file, you will be prompted to enter the name of a new one.
- Exit (Alt + E) This command exits the program. The program can also be closed using the X in the top right corner of the program window.
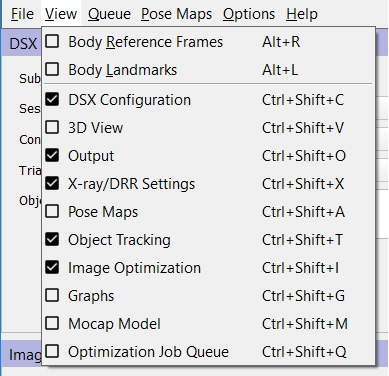
View Menu
- Body Reference Frames (Alt + R) toggles the display of the local coordinate systems of the selected objects in the X-ray windows and the 3D view.
- Body Landmarks (Alt + L) toggles the display of the landmarks of the selected objects in the X-ray windows and the 3D view.
- DSX Configuration (Ctrl + Shift + C) toggles the appearance of the dockable DSX Configuration widget, which lets you select sessions, configurations, trials, and objects.
- 3D View (Ctrl + Shift + V) toggles the appearance of the dockable 3D View window, which displays the X-ray configuration, selected objects, and mocap markers.
- Output (Ctrl + Shift + O) toggles the appearance of the dockable Output window, which shows informational and error messages.
- Xray/DRR Settings (Ctrl + Shift + X) toggles the appearance of the dockable Xray/DRR Settings widget, which gives you access to the settings used to process the X-ray and DRR images.
- Pose Maps (Ctrl + Shift + A) toggles the appearance of the dockable Pose Maps widget, which has commands for editing the pose maps.
- Object Tracking (Ctrl + Shift + T) toggles the appearance of the dockable Object Tracking widget, which lets you track objects in the X-ray images.
- Image Optimization (Ctrl + Shift + I) toggles the appearance of the dockable Image Optimization widget, which can be used to optimize the X-ray, DRR, and image metric settings to better track objects in the X-ray images.
- Graphs (Ctrl + Shift + G) toggles the appearance of the dockable Graphs widget, which displays the pose maps of the selected objects.
- Mocap Model (Ctrl + Shift + M) toggles the appearance of the dockable Mocap Model widget, which lets you apply the mocap model to the objects in the current trial.
- Optimization Job Queue (Ctrl + Shift + Q) toggles the appearance of the dockable Optimization Job Queue widget, which displays the currently loaded tracking optimization job queue.
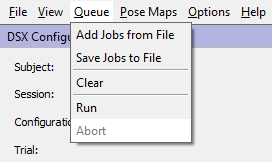
Queue Menu
- Add Jobs from File loads a job queue file (*.xjq). The jobs in the file are appended to the end of the queue.
- Save Jobs to File saves the current job queue to a file (*.xjq).
- Clear clears the current job queue (no undo!).
- Run runs all the jobs in the queue.
- Abort aborts a currently running job queue.
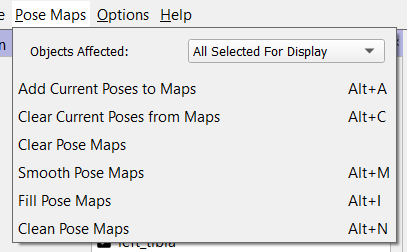
Pose Maps Menu
This menu provides the same functionality as the Pose Maps widget.
- Objects Affected Specifies the objects that are affected by the actions in this menu. Available options are: a) All Selected For Display and b) All Selected For Optimization.
- Add Current Pose to Maps (Alt + A) adds the current pose of each object specified in the Objects Affected combo box to its pose map.
- Clear Current Poses from Maps (Alt + C) removes the pose for the current time of each object specified in the Objects Affected combo box from its pose map.
- Clear Pose Maps removes all poses from the pose map for each object specified in the Objects Affected combo box.
- Smooth Pose Maps (Alt + M) smooths the poses in the tracking range for each object specified in the Objects Affected combo box, using the cutoff frequency specified in the graph widget.
- Fill Pose Maps (Alt + I) adds a pose for each reporting time in the tracking range that does not already have one to the pose map of each object specified in the Objects Affected combo box.
- Clean Pose Maps (Alt + N) removes all poses that are not at one of the trial's reporting times from the pose map of each object specified in the Objects Affected combo box.
Options Menu
- Settings… opens the Settings dialog window.
- Select GPUs… (Alt + G) opens a dialog window that lets you assign GPUs to the X-ray views.
Help Menu
- Help (F1) opens the X4D wiki page in the default browser.
- System Information… opens a dialog window with information about your computer, including available RAM and graphics card specifications.
- About… displays a dialog with information about X4D, including the installed version number. It also contains the Deactivate button, for deactivating your DSX suite license.
Widgets
The X4D application contains 13 different widgets: