Table of Contents
Regions of Interest
Regions of interest (ROIs) are portions of an object's surface model that have been labelled as belonging to a particular group. They are used to calculate distance maps for articulating bones by finding the shortest distance from each point in one ROI to the corresponding ROI on a neighboring bone.
Before defining ROIs on an object, it is important to define the local coordinate system (LCS) first. When ROIs are created, they are aligned with the LCS so that it is easier to interpret distance calculations, and to ensure that all ROIs on an object align with each other. Like the LCS algorithms, the ROIs are implemented in a dll plugin framework, allowing you to integrate your own ROI types.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
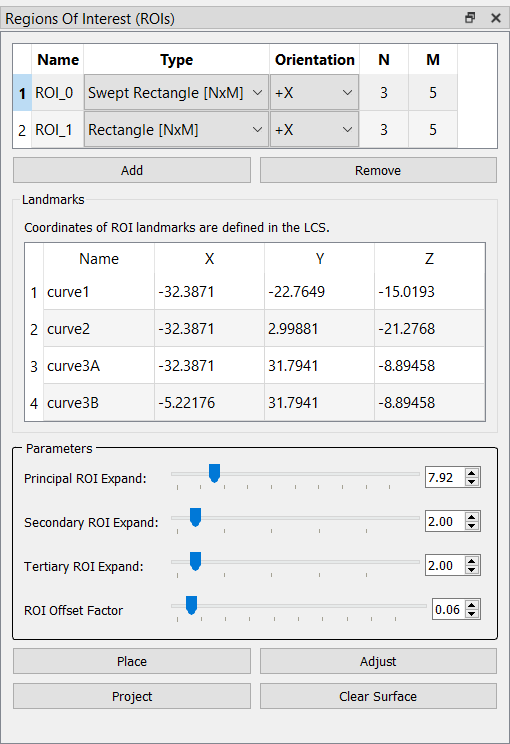
| Add | Creates a new ROI and adds it to the table. |
| Remove | Deletes the selected ROI, even if it has been placed (but not projected) on the surface model. However, if the ROI has already been projected, it does not remove it from the model. |
| Place | Displays the ROI floating above the surface model, based on the landmarks. You can then check and modify its positioning before actually projecting it onto the model. To assist with the positioning of the ROI, a yellow wire frame search box is displayed as well. The ROI is projected onto the portion of the surface model that is within this search box. The size of the search box can be adjusted using the parameters in the Parameters section. |
| Adjust | Enters and exits manual ROI adjustment mode. In this mode the placed ROI can be moved manually using the mouse buttons. The following interactions are defined: * Rotating about the ROI center - moving the mouse while pressing the left mouse button * Spinning - moving the mouse while pressing the left mouse button and the Ctrl key * Translation - moving the mouse while pressing the left mouse button and the Shift key or moving the mouse while pressing the middle mouse button * Scaling - moving the mouse while pressing the right mouse button Note that the yellow search box adjusts itself with the ROI. Pressing the Adjust button a second time exits manual adjustment mode. |
| Project | Projects the placed ROI onto the surface model. Each ROI subregion is projected along its normal to determine the polygons of the surface that it intersects. These polygons are labelled with that subregion's label. |
| Clear Surface | Clears all of the ROI labels from the surface model. |
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| Principal ROI Expand | The scale factor for the search box in the principal direction of the ROI. The principal axis depends on the type of ROI, but is roughly equal to the direction of projection. |
| Secondary ROI Expand | The scale factor for the search box along the width of the ROI. |
| Tertiary ROI Expand | The scale factor for the search box along the length of the ROI. |
| ROI Offset Factor | The amount to offset the ROI surface along the principal axis, specified as a percentage (0.0 to 1.0) of the maximum dimension of the object. The default value is 0.03. The principal axis depends on the type of ROI, but is roughly equal to the direction of projection. |
Region of Interest Methods
Two methods are implemented for defining ROIs.
Rectangle [NxM]
Rectangle [NxM] is a flat rectangular ROI whose normal vector is specified by the orientation parameter. It is divided into NxM subregions, and is projected onto the object along the negative of its orientation axis. Its initial placement on the object is specified by four landmarks: edge1, edge2, edge3, and edge4. These landmarks do not need to be placed in any specific order, or in any specific locations relative to each other. They are used to define the minimum and maximum extents of the ROI in the two non-principal dimensions in the object’s local coordinate system. For example, if the ROI’s orientation is +Z or -Z, then the minimum and maximum X and Y coordinates of the four landmarks define the ROI rectangle in the XY plane.
Swept Rectangle [NxM]
Swept Rectangle [NxM] is a curved rectangular surface divided into NxM subregions. It is useful for defining ROIs on curved bone surfaces such as the femoral condyles. Its placement is defined by four landmarks: curve1, curve2, curve3A, and curve3B. The first three landmarks define the arc along which the ROI is swept. They also define the direction with N subregions. Curve3B should be placed such that the vector from curve3A to curve3B is perpendicular to the arc, and along the orientation axis of the ROI. Curve3A and curve3B define the direction with M subregions and the distance between them defines the width of the ROI. When the ROI is projected, each subregion is projected along the negative of its normal. Because the normals of adjacent subregions along the length of the arc are not parallel, their projections on the object surface will overlap. In these cases the overlapping surface is bisected and divided equally between the two subregions.
Disk
Disk is a circular flat circular ROI whose normal vector is specified by the orientation parameter. It is divided into NxM subregions, and is projected onto the object along the negative of its orientation axis. Its placement is defined by two mandatory and two optional landmarks. The mandatory landmarks are Center and Outer Radius, which define the center and outer perimeter of the ROI, respectively. These mandatory landmarks also define the direction with N subregions.
The optional Inner Radius defines the radius of the hole inside the ROI, and the Pie Angle allows you to remove a pie-shaped slice from the disk. The slice is defined by the angle Pie Angle-Center-Outer Radius (the slice between Pie Angle and Outer Radius is removed).
ROIs in Visual3D
Visual3D can display these maps as color tables on the articulating bones then use these maps to graph shortest bone-to-bone distances during the trial.
Example Region of Interest
For example, on the distal femur it is common to define an ROI on the lateral condyle and another one on the medial condyle. On the proximal tibia, an ROI would cover the medial half of the plateau, and a second ROI would cover the lateral half. After both bones have been tracked for a motion trial, distance maps between the medial femur and medial tibia ROIs could be calculated, and the same for the lateral side.
See Also
Go back to the Orient3D Overview.