Table of Contents
Least Squares Fitting of Data
This page contains a list of all of Evaluate_Expression's functions that are used to find a line or plane of best fit to your data.
Best Fit Plane
Best_Fit_Plane(signal, start_event_signal, end_event_signal) - Finds a plane that fits the path of a point from a start event to an end event. The resulting plane is defined by 4 components.
The general form of the equation of a plane in 3D is ax+by+cz+d = 0 where 𝑎, 𝑏, and 𝑐 are the components of the normal vector which is perpendicular to the plane or any vector parallel to the plane.
If (𝑥0,𝑦0,𝑧0)is a point that lies on the plane, then 𝑑=−(𝑎𝑥0+𝑏𝑦0+𝑐𝑧0) and as 𝑎𝑥+𝑏𝑦+𝑐𝑧−(𝑎𝑥0+𝑏𝑦0+𝑐𝑧0)=0.
The result of the Best_Fit_Plane function is a signal with the fource components (a,b,c,d)
! Example: Compute a Best_Plane_Fit for one signal across a range of frames Evaluate_Expression /EXPRESSION=Best_Fit_Plane(CURRENT_SIGNAL,EVENT_LABEL::ORIGINAL::START,EVENT_LABEL::ORIGINAL::END) /SIGNAL_TYPES=TARGET /SIGNAL_FOLDER=ORIGINAL /SIGNAL_NAMES=LSK_1 /RESULT_TYPES=METRIC /RESULT_FOLDERS=PROCESSED /RESULT_NAME=LSK1_PLANE /APPLY_AS_SUFFIX_TO_SIGNAL_NAME=TRUE ;
! Example: Compute a Best_Plane_Fit for multiple signals at each frame of data Evaluate_Expression /EXPRESSION=Best_Fit_Plane(CURRENT_SIGNAL) /SIGNAL_TYPES=TARGET /SIGNAL_FOLDER=ORIGINAL /SIGNAL_NAMES=LSK_1+LSK_2+LSK_3 /RESULT_TYPES=DERIVED /RESULT_FOLDERS=PROCESSED /RESULT_NAME=LSK_PLANE /APPLY_AS_SUFFIX_TO_SIGNAL_NAME=TRUE ;
Best Fit Circle
Best_Fit_Circle(signal, start_event_signal, end_event_signal) - Fits a 2D circle to the path of a signal.
The algorithm computes a best fit plane to the data, rotates this plane into a principal plane, computes the center and radius, the rotates these values back into the original plane. The result is 4 components:
- the origin's X-coordinate;
- the origin's Y-coordinate;
- the origin's Z-coordinate; and
- the radius.
Best Fit Sphere
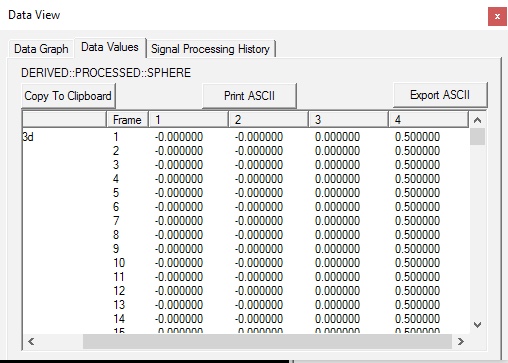
Best_Fit_Sphere(signal,start_event_signal,end_event_signal) - Fits a 3D sphere to the path of a signal.
! Example : Fit a sphere to 6 points on a DIAMOND ! Create 6 TARGETS representing the Vertices Create_Target /SIGNAL_NAMES=V1 ! /SIGNAL_DESCRIPTION= /EXPRESSION=VECTOR((0.5+0*FRAME_NUMBERS::ORIGINAL::FRAMES),0,0) ! /INCLUDE_CALFILE=FALSE ; Create_Target /SIGNAL_NAMES=V2 ! /SIGNAL_DESCRIPTION= /EXPRESSION=VECTOR((-0.5+0*FRAME_NUMBERS::ORIGINAL::FRAMES),0,0) ! /INCLUDE_CALFILE=FALSE ; Create_Target /SIGNAL_NAMES=V3 ! /SIGNAL_DESCRIPTION= /EXPRESSION=VECTOR((0,0.5+0*FRAME_NUMBERS::ORIGINAL::FRAMES),0) ! /INCLUDE_CALFILE=FALSE ; Create_Target /SIGNAL_NAMES=V4 ! /SIGNAL_DESCRIPTION= /EXPRESSION=VECTOR((0,-0.5+0*FRAME_NUMBERS::ORIGINAL::FRAMES),0) ! /INCLUDE_CALFILE=FALSE ; Create_Target /SIGNAL_NAMES=V5 ! /SIGNAL_DESCRIPTION= /EXPRESSION=VECTOR((0,0,0.5+0*FRAME_NUMBERS::ORIGINAL::FRAMES)) ! /INCLUDE_CALFILE=FALSE ; Create_Target /SIGNAL_NAMES=V6 ! /SIGNAL_DESCRIPTION= /EXPRESSION=VECTOR((0,0,-0.5+0*FRAME_NUMBERS::ORIGINAL::FRAMES)) ! /INCLUDE_CALFILE=FALSE ; Evaluate_Expression /EXPRESSION=Best_Fit_Sphere(CURRENT_SIGNAL) /SIGNAL_TYPES=TARGET /SIGNAL_FOLDER=ORIGINAL /SIGNAL_NAMES=V1+V2+V3+V4+V5+V6 /RESULT_TYPES=DERIVED ! /RESULT_FOLDERS=PROCESSED /RESULT_NAME=SPHERE ! /APPLY_AS_SUFFIX_TO_SIGNAL_NAME=FALSE ;
Note that TARGETS are created and the sphere computed has each TARGET on its surface.
! Example : Create a TARGET where each frame is on a random location on the surface of a sphere of radius 1 Evaluate_Expression /EXPRESSION=RAND(-PI(),PI(),FRAME_NUMBERS::ORIGINAL::FRAMES) /RESULT_TYPES=DERIVED /RESULT_FOLDERS=RADIUS /RESULT_NAME=VERTICAL ! /APPLY_AS_SUFFIX_TO_SIGNAL_NAME=FALSE ; Evaluate_Expression /EXPRESSION=RAND(0,2*PI(),FRAME_NUMBERS::ORIGINAL::FRAMES) /RESULT_TYPES=DERIVED /RESULT_FOLDERS=RADIUS /RESULT_NAME=HORIZONTAL ! /APPLY_AS_SUFFIX_TO_SIGNAL_NAME=FALSE ; Create_Target /SIGNAL_NAMES=SPHERE ! /SIGNAL_DESCRIPTION= /EXPRESSION=VECTOR( COS(DERIVED::RADIUS::VERTICAL)*COS(DERIVED::RADIUS::HORIZONTAL), -COS(DERIVED::RADIUS::VERTICAL)*SIN(DERIVED::RADIUS::HORIZONTAL), SIN(DERIVED::RADIUS::VERTICAL)) ! /INCLUDE_CALFILE=FALSE ; Evaluate_Expression /EXPRESSION=Best_Fit_Sphere(CURRENT_SIGNAL) /SIGNAL_TYPES=TARGET /SIGNAL_FOLDER=ORIGINAL /SIGNAL_NAMES=SPHERE /RESULT_TYPES=DERIVED ! /RESULT_FOLDERS=PROCESSED /RESULT_NAME=SPHERE ! /APPLY_AS_SUFFIX_TO_SIGNAL_NAME=FALSE ;
Simple Linear Regression
Simple_Linear_Regression(signal1, signal2, start_event, end_event); - Fits a signal to a line given by the equation Y = mX + b where
Signal = m Signal1 + b
An explanation of the calculation can be found here or here.
Signal1 and Signal2 are both one-component signals and the resulting METRIC contains 6 components:
- Slope = m → Component 1
- Intercept = b → Component 2
- Siga = uncertainty in m → Component 3
- Sigb = uncertainty in b → Component 4
- Chi2 = chi square → Component 5
- Q = The R^2 statistic → Component 6