Compute Volume Of Chest Wall
| Language: | English • français • italiano • português • español |
|---|
This command is based on the article by Ferrigno et al (1994) J Appl Physiol 77(3) 1224-1231.
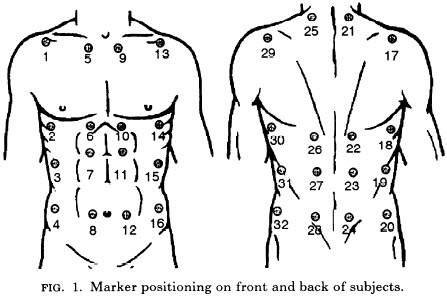
Marker Placement
The command expects all 32 vertices described in the article.
If any markers/landmarks are missing in a frame, no volume is computed.
Pipeline Command
- Compute_Volume_Of_Chest_Wall
- /SIGNAL_TYPES=TARGET
- /SIGNAL_NAMES=1+2+3+4+5+6+7+8+9+10+11+12+13+14+15+16+17+18+19+20+21+22+23+24+25+26+27+28+29+30+31+32
- /SIGNAL_FOLDER=ORIGINAL
- /RESULT_NAME=VOLUME
- ! /RESULT_FOLDER=PROCESSED
- ;
Units
Visual3D uses MKS units throughout the analyses. The only exceptions are joint angles which are represented in degrees.
The units for the volume are therefore m^3
Note that 1 m^3= 1000 liters
Compute_Volume_Of_A_Convex_Hull
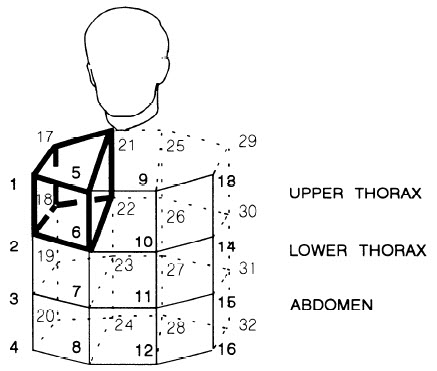
In Figure 2 the volume of the highlighted volume can be computed as a convex hull.
The volume of the chest wall is the sum of the volumes of the sub regions.
Output signal
The resulting signal contains two components. The first component is the volume The second component is the number of vertices that were available at that frame for computing the volume.