Sift - K-Means Dialog: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
<li><strong>Run Cumulative Variance Model</strong>: Can be used to determine the range of the K-Means test using variance explained instead of number of PCs</li> | <li><strong>Run Cumulative Variance Model</strong>: Can be used to determine the range of the K-Means test using variance explained instead of number of PCs</li> | ||
<li><strong>Number of PCs (1-25)</strong>: The number of principal components representing the workspace.</li> | <li><strong>Number of PCs (1-25)</strong>: The number of principal components representing the workspace.</li> | ||
<li><strong>Scale PC Scores to Variance Explained</strong>: Normalizes the scale on the workspace scores using the variance explained</li> | <li><strong>Scale PC Scores to Variance Explained</strong>: Normalizes the scale on the workspace scores using the variance explained</li> | ||
<li><strong>Use Custom Seed For First Centroid</strong>: Allows the selection of a custom seed instead of a randomly generated one, creates consistent results across runs.</li> | |||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
Latest revision as of 14:07, 30 April 2024
| Language: | English • français • italiano • português • español |
|---|
The K-Means button is found on the toolbar and under ![]() Outlier Detection.
Outlier Detection.
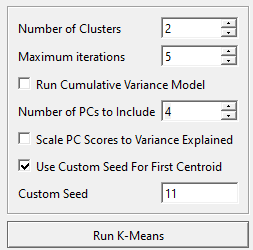
- Number of Clusters: The number of clusters to be calculated.
- Maximum iterations: How many times the calculations will be run, more iterations will refine the results at the cost of longer processing times.
- Run Cumulative Variance Model: Can be used to determine the range of the K-Means test using variance explained instead of number of PCs
- Number of PCs (1-25): The number of principal components representing the workspace.
- Scale PC Scores to Variance Explained: Normalizes the scale on the workspace scores using the variance explained
- Use Custom Seed For First Centroid: Allows the selection of a custom seed instead of a randomly generated one, creates consistent results across runs.
Running a K-Means Test
A more in depth guide on the uses of K-Means and how to run one can be found here.