Sift Tutorial: Outlier Detection with PCA
| Language: | English • français • italiano • português • español |
|---|
This tutorial will show you how to use the outlier detection methods built into Sift, when each method might be appropriate and how to interpret the results. Outlier detection is a key artifact of data analysis, identifying errant data or anomalies that might make further data analysis less effective. Within Sift, there are multiple methods for detecting outliers, but we will be focusing on doing so with PCA data in this tutorial.
Data
For this tutorial, we will be examining some data from a Visual3D Workshop at a recent ASB meeting. We first need to load the .CMZs into Sift (load from the V3D Workshop folder), and then create and calculate some queries. We will simply use the results from Sifts built in Auto Populate Queries dialog. Your load and explore pages should look as follows:
If you are having trouble with the above instructions, the Sift Tutorials wiki page has many tutorials that will help you out.
Local Outlier Factor
Local Outlier Factor(LOF) is a outlier detection method that uses the local density around data points to determine if a point is an outlier. In this sense it can find outliers that global detection methods would not, as it identifies outliers in local areas.
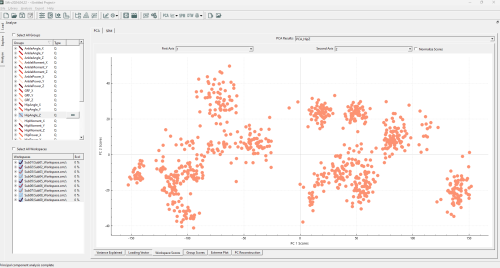
In Sift, LOF is built upon the PCA module, to find outliers in the PC workspace scores. As such, we will need to create a PCA analysis. To show the benefits of Local Outlier Factor, we will be using the group "HipAngle_Z", as it has a good shape to demonstrate the effectiveness of LOF (multiple clusters of varying density). Specifically, create a PCA on HipAngle_Z with all workspaces selected, 4 PCs calculated, "Use Workspace Mean" unchecked, and named "PCA_HipZ".
After calculating the PCA Results, the Workspace Scores on the analyse page should look as follows: